|
 Country report Hungary Country report Hungary
PROTECTED CULTIVATION IN HUNGARY
dr. ANDREA MOÓR
Hungarian representative
GENERAL INFORMATION
Geographical position: between latitude 45o45' -48o35' North nd longitude 16o05'-22o55' East.
The country is located in The Carpathian Basin. It is encircled by the Carpathians and DinaricAlps. Most than 70% of it's area is flat, only in the borders has some hills. The highest peak of the country is the Kékes. It is 1015 m high above sea level.
The country has two main rivers Danube and Tisza.
The country has commom borders with Austria, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia-Montenegro, Croatia and Slovenia
Total area: 93 030 km2
Population: 10 152 000
The population lives in 243 towns and 2893 villiges
Density of population: 109,2
Habitans of Capital (Budapest) 2 millions
Employment of Agriculture 6.2%
Industry 34.1%
Provision 59.7%
GDP/person 6938 USD
Climate: Climaticaly Hungary belongs to the continental climate.
Summer temperature is about 20days/year above 30oC.
Winter temperature is some time can reach - 20oC or less.
The average temperature from October to April 5.5oC
from May to September 17.6oC (Table 1.)
Table 1
Climate conditions of different protected cultivations area (an average 30 years)
1. area Szentes -Csongrád
|
Month |
I. |
II. |
III. |
IV. |
V. |
VI. |
VII. |
VIII. |
IX. |
X. |
XI. |
XII. |
|
Average temp.oC |
-1,8 |
0,9 |
5,6 |
11,1 |
16,2 |
19,2 |
20,8 |
20,2 |
16,5 |
11,0 |
5,1 |
0,6 |
|
Maximum oC |
1,7 |
5,1 |
11,2 |
17,1 |
22,3 |
25,3 |
27,4 |
27,0 |
23,4 |
17,6 |
9,5 |
3,8 |
|
Minimum oC |
-4,8 |
-2,5 |
0,9 |
5,5 |
10,3 |
13,4 |
14,4 |
13,9 |
10,4 |
5,6 |
1,7 |
-2,1 |
|
Hours of sunshine |
61 |
87 |
142 |
180180 |
234 |
255 |
288 |
266 |
210 |
170 |
80 |
51 |
2. area Middle of Hungary
|
Month |
I. |
II. |
III. |
IV. |
V. |
VI. |
VII. |
VIII. |
IX. |
X. |
XI. |
XII. |
|
Average temp.oC |
-1,7 |
0,8 |
5,6 |
11,0 |
16,1 |
19,2 |
20,6 |
20,2 |
16,3 |
10,8 |
4,8 |
0,6 |
|
Maximum oC |
1,5 |
4,8 |
11,0 |
16,9 |
22,3 |
26,1 |
27,4 |
26,3 |
22,4 |
15,6 |
9,3 |
3,5 |
|
Minimum oC |
-5,1 |
-2,5 |
0,9 |
5,4 |
10,1 |
13,3 |
14,0 |
13,9 |
10,4 |
5,6 |
1,4 |
-2,6 |
|
Hours of sunshine |
63 |
87 |
136 |
177 |
226 |
228 |
255 |
235 |
176 |
144 |
73 |
53 |
3. area Békés
|
Month |
I. |
II. |
III. |
IV. |
V. |
VI. |
VII. |
VIII. |
IX. |
X. |
XI. |
XII. |
|
Average temp.oC |
-2,6 |
0,2 |
5,1 |
10,7 |
15,8 |
18,7 |
20,3 |
19,6 |
15,8 |
10,3 |
4,5 |
-0,2 |
|
Maximum oC |
0,6 |
4,1 |
10,4 |
16,6 |
21,7 |
24,6 |
26,5 |
26,1 |
22,4 |
16,5 |
8,5 |
2,6 |
|
Minimum oC |
-5,5 |
-3,0 |
0,6 |
5,4 |
10,1 |
13,1 |
14,4 |
13,7 |
10,3 |
5,3 |
1,3 |
-2,8 |
|
Hours of sunshine |
55 |
84 |
137 |
182 |
230 |
248 |
274 |
255 |
197 |
156 |
67 |
48 |
4. area Jászság
|
Month |
I. |
II. |
III. |
IV. |
V. |
VI. |
VII. |
VIII. |
IX. |
X. |
XI. |
XII. |
|
Average temp.oC |
-1,6 |
1,1 |
5,6 |
11,1 |
15,9 |
19,0 |
20,8 |
20,2 |
16,4 |
11,0 |
4,8 |
0,4 |
|
Maximum oC |
1,2 |
4,5 |
10,2 |
16,3 |
21,4 |
24,4 |
26,5 |
26,0 |
22,1 |
16,1 |
8,1 |
3,1 |
|
Minimum oC |
-4,0 |
-1,7 |
1,7 |
6,3 |
10,8 |
13,9 |
15,4 |
14,9 |
11,5 |
6,7 |
2,1 |
-1,8 |
|
Hours of sunshine |
55 |
82 |
146 |
191 |
239 |
250 |
282 |
261 |
201 |
160 |
70 |
45 |
5. area Baranya
|
Month |
I. |
II. |
III. |
IV. |
V. |
VI. |
VII. |
VIII. |
IX. |
X. |
XI. |
XII. |
|
Average temp.oC |
-3,3 |
-0,5 |
4,4 |
10,3 |
15,2 |
18,3 |
19,9 |
19,1 |
15,2 |
9,4 |
3,7 |
-1,1 |
|
Maximum oC |
0,0 |
3,7 |
10,1 |
16,7 |
21,6 |
24,5 |
26,5 |
25,9 |
22,0 |
15,8 |
7,4 |
1,9 |
|
Minimum oC |
-6,3 |
-3,9 |
-0,6 |
4,3 |
9,0 |
12,3 |
13,6 |
13,0 |
9,5 |
4,5 |
0,7 |
-3,7 |
|
Hours of sunshine |
41 |
70 |
128 |
177 |
224 |
224 |
255 |
236 |
181 |
142 |
53 |
36 |
Cultivated area: Approximately 80% of the country's territory is suitable for agricultural production. The vegetables productions 14% of productive land area, and 18% of agricultural area. (Table 2.)
Table 2.
Cultivated area in Hungary (x1000 ha)
|
Branches of cultivation |
1998 |
2000 |
2002 |
|
Arable land |
4710 |
4500 |
4516 |
|
Gardens |
89 |
99 |
108 |
|
Agricultural area (total) |
6193 |
5854 |
5867 |
|
Productive land area (total) |
8036 |
7706 |
7732 |
|
Uncultivated area |
13,6 |
15,9 |
16,9 |
Datas by KSH
Land use
After the change of regime in Hungary , approximately 90% of the land is given into private hands. The farm size is between from 1 ha -to more than 100 ha-s.
In Hungary ,agricultural activities have great importance and increase year by year as shows a datas (Table3.)
Table3.
Export of agriculture (millionsUSD)
| |
2000 |
2003 |
|
Agriculture (total) |
255,89 |
667,84 |
|
Vegetables |
124,48 |
147,15 |
Datas by AKII
Protected cultivation in Hungary produces vegetables two different ways: One of them in the openfield and the other one on protected cultivation. (Table 4.)
Table 4.
Vegetable production in Hungary (ha)
|
Cultivation |
2000 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
|
Open field |
84 172 |
94 008 |
103 445 |
101 903 |
|
Protected |
5 300 |
5 145 |
5 170 |
5 185 |
|
Total |
89 472 |
99 153 |
108 615 |
107 088 |
Datas by Fruit and Vegetable Bulletin
Area of protected cultivation
There are five main areas where producing vegetables under greenhouses or plastic tunnels and with mulch. (Fig. 1)
Fig. 1: THE MAIN PROTECTED AREAS IN DIFFERENT REGIONS OF HUNGARY
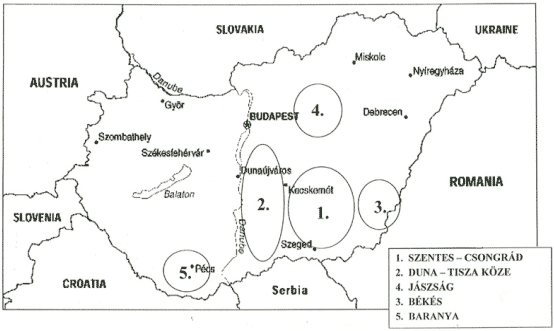
- The southern part of Hungary (Szentes, Csongrád)
This area has many of geothermicwater most of them in use for greenhouse heating. The wells depth changes between 1200-2200m and the water temperature is between 76oC and 98oC. This area has the most glasshouse (80 ha-s) and high plastic tunnels (walk-in-tunnel 1 800 ha-s). Also there are low-tunnels (100 ha-s) and different kinds of simple covers such as agryl or plastic mulch (120 ha-s). All of greenhouses have heating systems and 30% of hightunnels have it.
- Middle of Hungary.(from Budapest -to Szeged)
This area previously has only low tunnels nowadays more and more walk-in tunnels (800ha-s)and greenhouses(18 ha-s) such us Rischel and Filclair (4,2 ha-s).
- The Eastern part of Hungary nex to the Romanian border (Békés) has 18 ha-s glasshouses, 3,4 ha-s Rischel house and 280 ha-s walk-in tunnels. This area has the most agryl mulch (3800 ha-s).
- The northernpart of Hungary. It is located 60-70 km far from Budapest.The name is Jászság. Here the most important structure is a walk-in tunnel (1200 ha-s) usually without heating and 2500 ha-s agryl mulch.
- The southwestern part of Hungary next to the Croatian border (Baranya) has traditional low tunnels (460 ha-s) and 1200 ha-s agryl mulch covering.
Table 5.
Protected vegetable production by species
|
Species |
2000 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
|
Pepper (paprika) |
2350 |
2400 |
2380 |
2300 |
|
Tomato |
1100 |
1100 |
1090 |
1120 |
|
Cucumber |
520 |
510 |
480 |
435 |
|
Cabbage |
420 |
260 |
300 |
400 |
|
Savoy cabbage |
90 |
75 |
60 |
70 |
|
Chinese cabbage |
100 |
60 |
80 |
90 |
|
Cauliflower |
160 |
150 |
150 |
140 |
|
Carrot |
380 |
390 |
410 |
400 |
|
Parsley |
180 |
200 |
220 |
230 |
Datas by Fruit and Vegetable Bulletin
Season of protedted cultivation
Thre are 4 different season of protected cultivation in Hungary.
- „winter crop":It is growing under a glasshouse and special geenhouse such as Rischel (Fig.2) and Filclair with different kinds of heating systems. The sowing date for this cultivation is September, October. Transplanting date is November, December. The harvest season is from January-to July it is depend of crops. Used species: pepper, tomato, cucumber
Fig. 2: Rischel house with heating system and double plastic covering

- „early forcing": It is growing under walk-in tunnel (double or more plastic covered Fig. 3-4) with different kinds of heating systems. The sowing date is November, December, transplantig is February, March. Harvest season is from April to July. Cultiveted crops: pepper, tomato and different kinds of cabbeges.
Fig. 3. High tunnel with double plastic covered and low tunnel inside ((closed)

Fig. 4: Inside low tunnel open during day time

unheated forcing" All kinds of plastic tunnel used for it. (Fig. 5). The sowing date is February, March it is depend of crops. Transplanting from April and growing season is to November, some time only to August depends the crop price. Cultiveted crops are: pepper, different kinds of cabbeges and very few tomato.
Fig. 5.Unheated tunnel covered with rascel (protected to sun)

- „autum crop" We can use for it a glasshouse and a walk-in tunnel generally without heating, but if the temperature dramaticaly going down possible use some kind of heating system. Sowing date is Jun, July, transplanting August, September. The cultivation period to December. Used crops are pepper, tomato and lettuce.
Plastic and agryl mulch are using on open field for protection such as low temperature on different kinds of melon (80% watermelon) Fig. 6.
Lots of unheated walk-in tunnel cultivated with carrot and parsley sme times cellary.
Fig. 6: Watermelon production covered with plastic mulch

Yield, types and cultivars
We have many of years traditional with protected cultivation. The last 10-15 years the farmers use the update varities not only Hungarian breed, but all of varieties of foreign seed company too. That is mean the yield is stabil as you see on the Table 5.
Table 6.
Yield of protected cultivation (1000 to)
|
Species |
2000 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
|
Pepper |
180 |
188 |
185 |
178 |
|
Tomato |
98 |
100 |
100 |
104 |
|
Cucumber |
84 |
80 |
74 |
59 |
|
Cabbege |
23 |
15 |
17 |
18 |
|
Savoy cabbege |
2,1 |
2,5 |
1,9 |
2,4 |
|
Chinese cabbege |
3,0 |
1,7 |
2,5 |
2,8 |
|
Cauliflower |
3,2 |
3,0 |
3,0 |
2,9 |
|
Carrot |
12 |
13 |
14 |
13 |
|
Parsley |
5,1 |
5,4 |
6,0 |
5,2 |
Datas by Fruit and Vegetable Bulletin
Pepper production: In Hungary we have special Hungarian type „sweet, whithe conical".(Fig.7.) Hundred % of this types were breed by Hungarian Institute or Hungarian private seed company. Also we growing „hot, long" type pepper (Fig.8.) too, before it was also Hungarian breed nowadays some Duth company also have the same type.
All to others vegetable varieties 80-85 % come from foreign seed companies.The farmers use year by year the update varieties, because all seed company has representatives in Hungary. They are every year organized some demonstration for the farmers and shows them a new varieties.
Technology
Hungary has a very good soil conditionseven the areaswhere using a protected cultivation. Growers used indoor greenhouseculture for a long time. As a results of monocultureproduction many problem appeared:soils had poor structure, high level of nutriens and many problem with diaseases. Usually these areas were disinfection different way On one hand by steam (under glasshouses) and the other hand by chemicals. As you know the chemicals is prohibited from 2005. It is mean the farmers have to change a technology. The most biggest glasshouse area and some farmer changed the growing system to soilless culture. (Nowadays 30 ha-s greenhouses have it). This technology need more input (money, knowledge etc.) than usually the Hungarian farmers have.
Most protected cultivation area is between 1000m2-3000m2. Some examination shows us under the 3500 m2 of soilless culture is not profitable in this moment in Hungary (by Tompos). Because the energy costs and the others (fertilizer,labor cost etc.) increase year by year and we have lot of cheap vegetable import from the southern countries (Spain, Greece, Italy, Morocco).
How to go to the future?

must be stop
small size of the growing area (minimum size is about 3000 m2)
selling alone (as you know in EU financiall support only for the producer organization )
increase the quality
increase the quantity
There are many of big chain of stores,who needs a same quality and huge quantity all year from the farmers
competition in a market

possibility to get more financial support --› increase the technical develop into greenhouse structure
possibility togo to the EU market by producer organization
must be organization between all producer countries
have to find a place for a product
In EU producing 54 millions to vegetables from itHungary producing 1.8 millions to (3.5 %).
The market is full of ordinary vegetables. We can be valid if we can produce special product (best quality,"hungaricum", etc.) in special time.
|

